Osteology
|
| Bone |
Structure |
Description |
Notes |
| pubis (TG6-03, TG6-03) |
|
an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis |
one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its body forms 1/5 of the acetabulum; its symphyseal surface unites with the pubis of the opposite side to form the pubic symphysis; the superior and inferior pubic rami participate in the formation of the obturator foramen |
|
inferior ramus |
inferior "limb" that passes inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis |
articulates with the ischial ramus to form the ischiopubic ramus; attachment site for the root of the penis (clitoris) (Latin, ramus = a branch) |
| pubic symphysis (N248, TG5-03) |
the midline joint uniting the superior rami of the two pubic bones |
a symphysis; a fibrocartilage interpubic disk unites the bones; the subpubic angle (at the pubic arch) in the female is greater than the subpubic angle in the male |
(Greek, symphysis = a growing together) |
ischium (N486, TG3-04) |
|
the "V"- shaped bone that forms the posteroinferior part of the pelvis |
one of the three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis |
| |
ischial ramus |
the limb of the ischium that passes anteriorly and superomedially toward the pubis |
it articulates with the inferior ramus of the pubis to form the ischiopubic ramus (Greek, ischion = hip joint; Latin, ramus = a branch) |
|
ischial tuberosity |
the roughened projection that protrudes posteroinferiorly from the body of the ischium |
it is the site of attachment of the sacrotuberous ligament; it is the site of origin of the inferior gemellus m., quadratus femoris m. and the hamstring mm. (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, long head of biceps femoris, ischiocondylar portion of the adductor magnus) (Greek, ischion = hip joint) |
|
lesser sciatic notch |
the notch located between the ischial tuberosity and the ischial spine |
the lesser sciatic notch is converted to the lesser sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament |
|
ischial spine |
the spine that arises just superior to the lesser sciatic notch |
it is the site of attachment of t he sacrospinous ligament and the site of origin of the superior gemellus m. (Greek, ischion = hip joint) |
| ilium (N486, TG3-04) |
|
fan-shaped bone that forms the lateral prominence of the pelvis |
one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis |
|
greater sciatic notch |
the notch on the inferior portion of ilium located posteromedial to the ischial spine |
the greater sciatic notch is converted to the greater sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament |
| coccyx (N248, TG5-03) |
|
the most inferior portion of the vertebral column |
the coccyx results from the fusion of the four coccygeal vertebrae; it may be a single bone or the first coccygeal vertebra may be separated from the other three; it articulates with the fifth sacral segment; coccygeal vertebrae are reduced in complexity, having no pedicles, laminae or spines (Latin, coccyx = a crow's beak) |
Muscles
|
| Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Action |
Innervation |
Artery |
Notes |
Image |
| anal sphincter, external (N390, N392, N393, N394, TG6-15, TG6-27) |
perineal body or central tendinous point of the perineum |
encircles the anal canal; superficial fibers attach to the coccyx |
constricts the anal canal |
inferior rectal nerves (from the pudendal nerve) |
inferior rectal a. |
skeletal (voluntary) muscle, as contrasted with sphincter ani internus, which is smooth (involuntary) muscle; the external anal sphincter is considered part of the pelvic diaphragm (Greek, sphincter = that which binds tight) |
 |
| bulbospongiosus, in female (N379, N382, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
perineal body and fascia of the bulb of the vestibule |
perineal membrane and corpus cavernosum of the clitoris |
compresses the vestibular bulb and constricts the vaginal orifice |
deep branch of the perineal nerve (from pudendal nerve) |
perineal a. |
skeletal muscle |
 |
| ischiocavernosus (N379, N382, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
medial surface of the ischial tuberosity and the ischiopubic ramus |
corpus cavernosum and crus of the penis/clitoris |
compresses the corpus cavernosum |
deep branch of the perineal nerve (from pudendal nerve) |
perineal a. |
ischiocavernosus m. is closely applied to the surface of the crus penis/clitoris |
 |
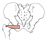
| obturator internus (N358, N360, N379, TG6-21, TG6-21, TG3-28) |
the internal surface of the obturator membrane and margin of the obturator foramen |
greater trochanter on its medial surface above the trochanteric fossa |
laterally rotates and abducts the thigh |
nerve to the obturator internus m. |
obturator a. |
the obturator internus m. leaves the pelvis by passing through the lesser sciatic foramen; the superior and inferior gemellus mm. insert on the obturator internus tendon |
 |
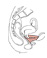
| sphincter urethrae, in female (N361, N366, N379, N382, N385, TG6-08, TG6-10, TG6-28A, TG6-28B) |
encircles the urethra |
encircles urethra and vagina; extends superiorly along the urethra as far as the inferior surface of the bladder |
compresses urethra and vagina |
deep branch of perineal nerve from pudendal nerve |
internal pudendal a. |
skeletal muscle (Greek, sphincter = that which binds tight) |
 |
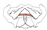
| superficial transverse perineus |
medial surface of the ischial ramus |
contralateral muscle and the perineal body/central tendinous point |
fixes and stabilizes perineal body/central tendinous point |
deep branch of perineal nerve from pudendal nerve |
perineal a. |
superficial and deep transverse perineus muscles are separated by the perineal
membrane |
 |
| deep transverse perineus |
medial surface of the ischial ramus |
contralateral muscle and perineal body/central tendinous point |
fixes and stabilizes the perineal body/central tendinous point |
deep branch of perineal nerve from pudendal nerve |
internal pudendal a. |
superficial and deep transverse perineus muscles are separated by the perineal
membrane |
 |
Nerves
|
| Nerve |
Source |
Branches |
Motor |
Sensory |
Notes |
| anterior labial n. (TG6-19A) |
ilioinguinal n. |
no named branches |
none |
skin of the anterior aspect of the labium majus |
communicates with the genital br. of the genitofemoral n. (Latin, labial = lips) |
| dorsal n. of the clitoris (TG6-19A) |
pudendal n. |
no named branches |
sympathetic motor innervation to skin |
skin of the shaft of the clitoris |
the terminal branch of the pudendal n. |
| inferior rectal n. (TG6-19A) |
pudendal n. |
no named branches |
external anal sphincter |
skin of the anus |
inferior rectal nerve is one of the first branches of the pudendal n. |
| perineal n. (TG6-19B) |
pudendal |
posterior scrotal/labial n., deep (muscular) br. |
muscles of the perineum: bulbospongiosus m., ischiocavernosus m., superficial and deep transverse perineus mm., sphincter urethrae m., sphincter urethrovaginalis, compressor urethrae |
skin of the posterior surface of the scrotum/labium majus |
perineal n.branches from the pudendal n. at the posterior margin of the transverse perineal muscles |
| plexus, rectal (TG6-19B) |
inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus, posterior part |
no named branches |
sympathetic: vascular smooth muscle of the pelvic viscera, especially the rectum; parasympathetic: smooth muscle and glands of the pelvic viscera, especially the rectum |
pain and general sensation from the rectum |
rectal plexus is continuous with the vesical plexus in the male, uterovaginal plexus in the female (Latin, plexus = a braid. A network of nerves, blood vessels, or lymphatic vessels) |
| plexus, vesical (TG6-19B) |
inferior hypogastric plexus |
continuous with the prostatic plexus |
sympathetic: vascular smooth muscle of the pelvic viscera, especially the urinary bladder, seminal vesicle, ductus deferens and ejaculatory duct; parasympathetic: smooth muscle and glands of the pelvic viscera, especially the urinary bladder, seminal vesicle, ductus deferens and ejaculatory duct |
pain and general sensation from the bladder, seminal vesicle and ductus deferens |
vesical plexus is continuous with the other autonomic nerve plexuses in the pelvis and cannot be distinguished from them (Latin, plexus = a braid. A network of nerves, blood vessels, or lymphatic vessels) |
| posterior labial n. (TG6-19A) |
perineal n. (a branch of the pudendal n.) |
no named branches |
none |
skin of the posterior aspect of the labium majus |
communicates with the perineal br. of the posterior femoral cutaneous n. (Latin, labial = lips) |
| pudendal n. (N404, N405, TG6-28A, TG6-28B, TG6-29A, TG6-29B, TG6-30A, TG6-30B) |
ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S2-S4 (sacral plexus) |
inferior rectal n., perineal n., dorsal n. of the clitoris/penis |
its branches supply: external anal sphincter, bulbospongiosus m., ischiocavernosus m., superficial & deep transverse perineus mm., sphincter urethrae m., sphincter urethrovaginalis, compressor urethrae |
its branches supply: skin of the anus, posterior scrotum/labium majus, clitoris/penis |
pudendal n. passes through the pudendal canal formed by fascia on the medial surface of the obturator internus m. (Latin, pudendus = ashamed, the term referred to "the shameful parts", ie the genitals) |
| uterovaginal plexus (TG6-19A) |
inferior hypogastric plexus |
continuous with the rectal plexus |
sympathetic: vascular smooth muscle of the pelvic viscera, especially the uterus, uterine tubes and vagina; parasympathetic: smooth muscle and glands of pelvic viscera, especially uterus, uterine tubes and vagina |
pain from the pelvic viscera listed at left |
the uterovaginal plexus is a subsidiary plexus of the inferior hypogastric plexus (Latin, plexus = a braid. A network of nerves, blood vessels, or lymphatic vessels) |
Arteries
|
| Artery |
Source |
Branches |
Supply to |
Notes |
| of bulb of vestibule |
internal pudendal a. |
no named branches |
bulb of the vestibule and associated tissues |
artery of the bulb of the vestibule courses within the deep perineal space to enter the deep surface of the bulb |
| clitoris, deep a. of (N404, N405, TG6-29A, TG6-29B, TG6-30A, TG6-30B) |
internal pudendal a. |
no named branches |
corpus cavernosum of the clitoris |
deep a. of the clitoris and dorsal a. of the clitoris are the terminal brs. of the internal pudendal a. |
| clitoris, dorsal a. of (N404, N405, TG6-29A, TG6-29B, TG6-30A, TG6-30B) |
internal pudendal a. |
no named branches |
superficial structures of the clitoris |
dorsal a. of the clitoris and deep a. of the clitoris are the terminal brs. of the internal pudendal a. |
| inferior rectal (TG6-28B, TG6-31B) |
internal pudendal a. |
no named branches |
anus, ischioanal fossa |
inferior rectal a. anastomoses with the middle rectal a. and the superior rectal a. |
| internal pudendal (N404, N405, TG6-28A, TG6-28B, TG6-29A, TG6-29B, TG6-30A, TG6-30B)
|
internal iliac a., anterior division |
inferior rectal a., perineal a., artery of the bulb of the clitoris/penis, urethral a., deep clitoral/penile a., dorsal clitoral/penile a. |
anus, muscles of the superficial and deep perineal spaces, clitoris/penis, posterior aspect of the scrotum/labium majus |
internal pudendal a. is the primary blood supply to the perineum |
| perineal (TG6-29A, TG6-29B) |
internal pudendal a. |
posterior labial/scrotal; deep br. |
posterior aspect of the scrotum/labium majus; muscles of the superficial perineal space |
perineal a. courses superficial to the superficial transverse perineus m.; it courses with the perineal n. |
| posterior labial (TG6-29A) |
perineal a. |
no named branches |
posterior aspect of the labium majus |
posterior labial a. courses through the superficial perineal space |
Viscera
|
| Organ/Part of Organ |
Location/Description |
Notes |
| clitoris (N377, TG6-25) |
combination of 3 erectile bodies: glans clitoris and 2 corpora cavernosa clitoris |
clitoris is covered by smooth skin |
| corona of the glans (N382) |
margin of the glans projecting beyond the ends of the corpora cavernosa |
overhangs the neck of the glans that separates the body from the glans of the penis |
| external urethral meatus (orifice) (female) (N377, TG6-25) |
opening of the membranous urethra into the vestibule of the vagina between the clitoris and the vaginal orifice |
|
| frenulum (N377, TG6-25)
|
a more posterior or deeper part of the labia minora passing posterior to the clitoris |
(Latin, frenulum = bridle, a narrow reflection of membrane from the lower surface of the glands with the prepuce) |
| glans penis/clitoridis (N377, TG6-25, N382) |
expanded distal end of the corpus spongiosum which caps the ends of the corpora cavernosa |
(Latin, glans = acorn) |
| hymen |
thin, usually incomplete septum at the inferior vaginal orifice |
the hymen is the remnant of the urogenital septum of the embryo, and the hymeneal caruncles are remnants of the hymen (Greek, hymen = a membrane) |
| labia majora (N377, TG6-25) |
fat-filled elevations of hair-covered skin lying on either side of the vestibule of the vagina |
labia majora are joined across the midline by the anterior and posterior labial commissures; they blend into each other anteriorly to form the mons pubis (Latin, labia = lips) |
| labia minora (N377, TG6-25) |
paired folds of hairless skin located medial to the labia majora and extending posteroinferiorly from the clitoris |
the anterior end of each labium minus divides: the anterior division of each labium forms the prepuce of the clitoris and the posterior division of each labium forms the frenulum of the clitoris (Latin, labia = lips) |
| mons pubis (N377, TG6-25) |
rounded, fatty prominence anterior to the pubic symphysis |
(Latin, mons = mountain) |
| prepuce (N377, TG6-25) |
fold of smooth skin extending over the glans penis/clitoris |
the anterior divisions of the labia minora combine to form the prepuce of the clitoris (Latin, praeputium = foreskin) |
| urethra (NN366, TG6-10, N378, TG6-10, N385) |
duct that drains the urinary bladder |
urethra has three parts in the male: prostatic, membranous & penile/spongy; female urethra is much shorter than the male urethra, consisting of the membranous part only |
| urethra, membranous (N385) |
part of the urethra that passes through the sphincter urethrae muscle and perineal membrane |
female: membranous urethra connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral orifice at the vestibule of the vagina; male: membranous urethra connects the prostatic urethra with the spongy/penile urethra |
| vagina (N377, TG6-25) |
part of the female genital canal located between the vestibule and the cervix |
vaginal fornices surround the cervix; the word "vagina" is derived from the Latin word for sheath |
| vestibule of the vagina (N377, TG6-25) |
region inferior to the hymen/hymeneal caruncles and between the labia minora |
vestibule of the vagina contains the external urethral orifice, the opening of the vagina and the openings of the greater vestibular glands |
| vulva (N377, TG6-25) |
serves as sensory and erectile tissue for sexual intercourse and arousal, directs the flow of urine, prevents entry of foreign material into the urogenital tract |
clinically called the pudendum |
| bulb of the vestibule (TG6-27A) |
erectile tissue located on either side of the vestibule of the vagina, attached to the perineal membrane |
bulb of the vestibule is continuous with the glans clitoris; it is covered on its superficial surface by the bulbospongiosus muscle; it is the homologue of the bulb of the penis |
| corpus cavernosum (N379, N382, N418, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
primary erectile bodies (paired) of the penis and clitoris |
corpora cavernosa attach via the crura to the ischiopubic rami and the perineal membrane; each crus is covered by an ischiocavernosus muscle; supplied by the deep a. of the penis/clitoris (Latin, corpus = body) |
| crus clitoris (N379, N382, N418, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
lateral part of the corpus cavernosum which is attached to the ischiopubic ramus and the perineal membrane |
crus clitoris is covered on its superficial surface by the ischiocavernosus muscle (Latin, crus = resembles a leg, therefore any structure which resembles a leg. The clitoris and diaphragm are two among many anatomical structures which take origin from crura) |
| erectile tissue (N379, N382, N418, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
tissue within the corpora cavernosa |
erection occurs as a result of blood filling the spaces of the corpora cavernosa |
| fascia, deep penile/clitoral |
an extension of the muscular fascia of the ischiocavernosus m. and bulbospongiosus m. onto the shaft of penis/clitoris |
deep fascia of the penis/clitoris forms a tubular sheath surrounding the erectile bodies, dorsal n. of the penis/clitoris, dorsal a. of the penis/clitoris, deep dorsal v. of the penis/clitoris; the superficial dorsal v. of penis/clitoris lies superficial to the deep fascia of the penis/clitoris; deep fascia of the penis is also known as: Buck's fascia |
| glans penis/clitoridis (N379, N382, N418, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
expanded distal end of the corpus spongiosum which caps the ends of the corpora cavernosa |
(Latin, glans = acorn) |
| greater vestibular gland (N379, TG6-27A) |
an exocrine gland located in the superficial perineal space posterior to the bulb of the vestibule |
greater vestibular gland is covered by the bulbospongiosus muscle; it produces a mucous secretion that drains into the vestibule of the vagina for lubrication of the vulva |
| perineal membrane (N381, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
membrane stretching across the urogenital triangle attaching to both ischiopubic rami |
perineal membrane is pierced by the urethra, vagina and branches of the pudendal neurovascular bundle |
| perineal body (TG6-27A) |
fibrous connective tissue in the midline between the vestibule of the vagina and the anus |
many of the muscles of the perineum attach at or to the perineal body, including the transverse perineal muscles, bulbospongiosus, and external anal sphincter; the male version is often called the central tendinous point |
| suspensory ligament of the penis/clitoris (TG6-31BA) |
a specialization of deep fascia connecting the proximal end of the penis/clitoris to the pubis and pubic symphysis |
the fundiform ligament is a specialization of superficial fascia that lies superficial to the suspensory ligament |
| tunica albuginea, corpus cavernosum (N379, N382, N418, TG6-27A, TG6-27B) |
outer white fibrous covering of the corpus cavernosum of the penis/clitoris |
tunica albuginea is a dense connective tissue layer that is not distensible, causing erection when the corpus cavernosum becomes engorged with blood (Latin, tunica albuginea = white coat + corpus = body) |
| urethra (N388, TG6-09A, TG6-09B) |
duct that drains the urinary bladder |
urethra has three parts in the male: prostatic, membranous & penile/spongy; female urethra is much shorter than the male urethra, consisting of the membranous part only |
| urethra, membranous (N388, TG6-09A, TG6-09B) |
part of the urethra that passes through the sphincter urethrae muscle and perineal membrane |
female: membranous urethra connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral orifice at the vestibule of the vagina; male: membranous urethra connects the prostatic urethra with the spongy/penile urethra |








